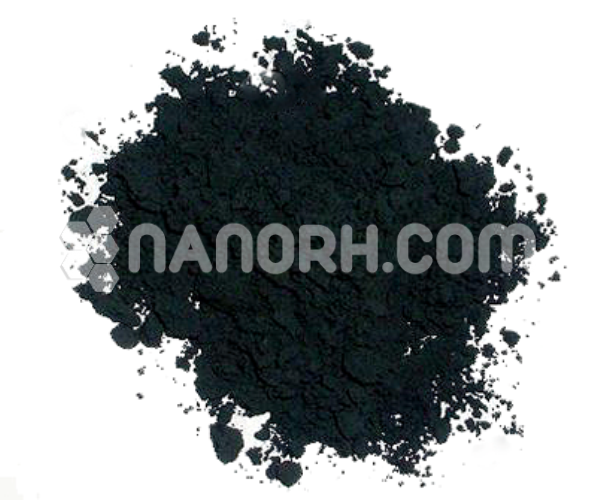
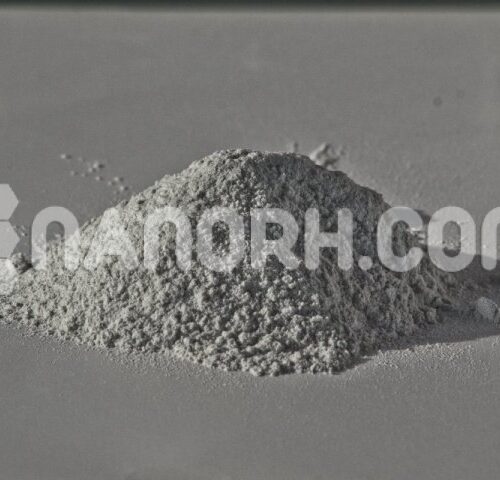
| Cobalt Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-29009 |
| CAS No. | 7440-48-4 |
| Formula | Co |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Gray |
| Molecular Weight | 58.93 g/mol |
| Density | 8.9 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1495 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2870 °C |
Cobalt Powder
Cobalt powder is a fine, granular form of cobalt metal, typically produced by processes such as reduction of cobalt salts or electrochemical methods. It is a versatile material known for its excellent strength, magnetic properties, and high resistance to wear and corrosion.
Applications
Cobalt Alloys:
Superalloys: Cobalt powder is a key component in the production of superalloys used in industries requiring materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as in jet engines, gas turbines, and power plants. These alloys provide exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability.
High-performance alloys: Cobalt-based alloys, such as cobalt-chromium and cobalt-molybdenum alloys, are used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors, particularly in applications like turbine blades, exhaust systems, and implantable medical devices.
Magnetic Materials:
Permanent magnets: Co is used in the production of permanent magnets, particularly in high-performance applications such as electric motors, hard disk drives, and magnetic sensors. Alloys like samarium-cobalt (SmCo) and cobalt-samarium are widely used due to their high magnetic strength and resistance to demagnetization.
Magnetic recording: Cobalt powder is used in the production of magnetic recording materials, such as those in hard disk drives and tape storage systems. The fine powder is able to produce high-density magnetic recordings.
Catalysis:
Hydrogenation and petroleum refining: Cobalt powder is widely used as a catalyst in the petroleum industry, particularly in hydrogenation reactions for converting unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated hydrocarbons. It also plays a key role in processes like Fischer-Tropsch synthesis for converting syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide) into liquid fuels and other chemicals.
Chemical synthesis: Cobalt powder is used in a variety of other catalytic processes, including the production of synthetic fuels, chemicals, and materials.
Batteries and Energy Storage:
Lithium-ion batteries: Cobalt powder is an essential component in lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion batteries), particularly in the production of cathodes. Cobalt enhances the performance, capacity, and stability of these batteries, making them suitable for use in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems.