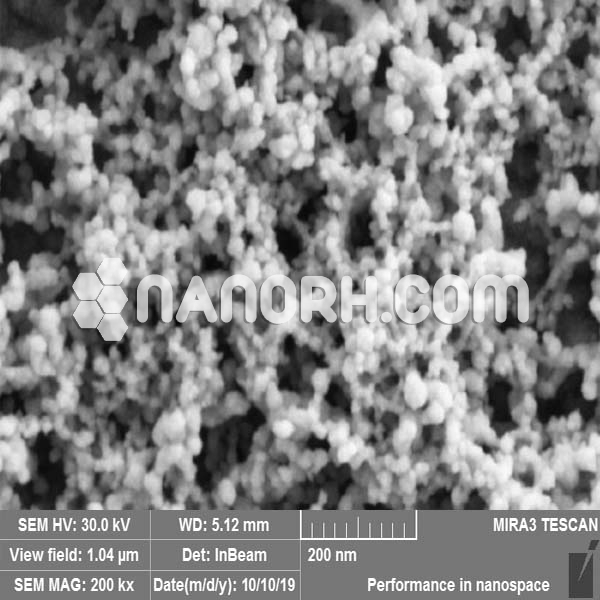
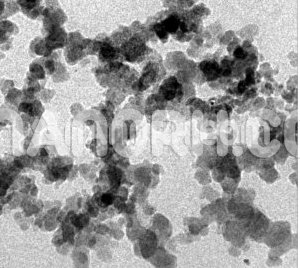
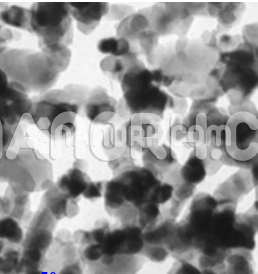
Cu-Zn Alloy Nanopowder / Nanoparticles (99.9%, <100 nm)
Copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve varying mechanical and electrical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other within the same crystal structure.
In contrast, bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Both bronze and brass may include small proportions of a range of other elements including arsenic, lead, phosphorus, aluminum, manganese, and silicon. The distinction is largely historical. Modern practice in museums and archaeology increasingly avoids both terms for historical objects in favor of the all-embracing “copper alloy”.
| Cu-Zn Alloy Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE- 2014 |
| CAS No. | 7440-50-8/7440-66-6 |
| Formula | Cu-Zn |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Grey-black |
| Molecular Weight | 128.926 g/mol |
| Density | 1.17 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 870°C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Cu-Zn Alloy Nanopowder
Cu-Zn Alloy Nanopowder / Nanoparticles
Copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve varying mechanical and electrical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other within the same crystal structure.
In contrast, bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Both bronze and brass may include small proportions of a range of other elements including arsenic, lead, phosphorus, aluminum, manganese, and silicon. The distinction is largely historical. Modern practice in museums and archaeology increasingly avoids both terms for historical objects in favor of the all-embracing “copper alloy”.
Brass is used for decoration for its bright gold-like appearance; for applications where low friction is required such as locks, gears, bearings, doorknobs, ammunition casings and valves; for plumbing and electrical applications; and extensively in brass musical instruments such as horns and bells where a combination of high workability (historically with hand tools) and durability is desired. It is also used in zippers. Brass is often used in situations in which it is important that sparks not be struck, such as in fittings and tools used near flammable or explosive materials.