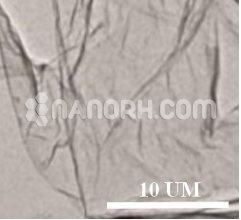
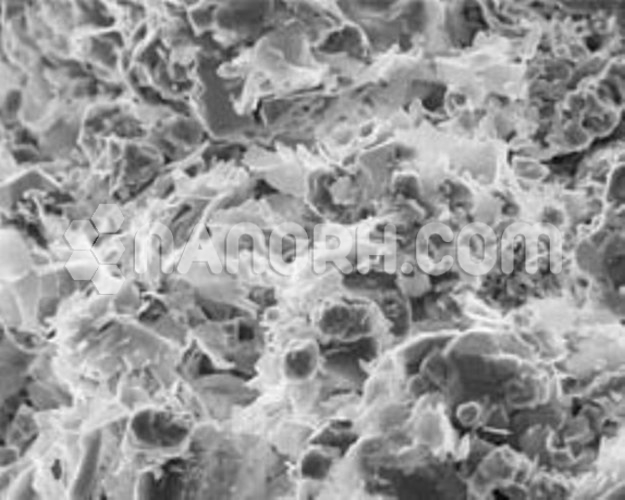
| Graphene Nanoplatelets Water Dispersion | |
| Product No | NRE-39010 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Purity | 95% |
| Average Diameter | 4-12um |
| Average Length | NA |
| Special Surface Area(SSA) | 500 – 1200m2/g |
| Tap Density | NA |
| True Density | NA |
| Electric Conductivity | NA |
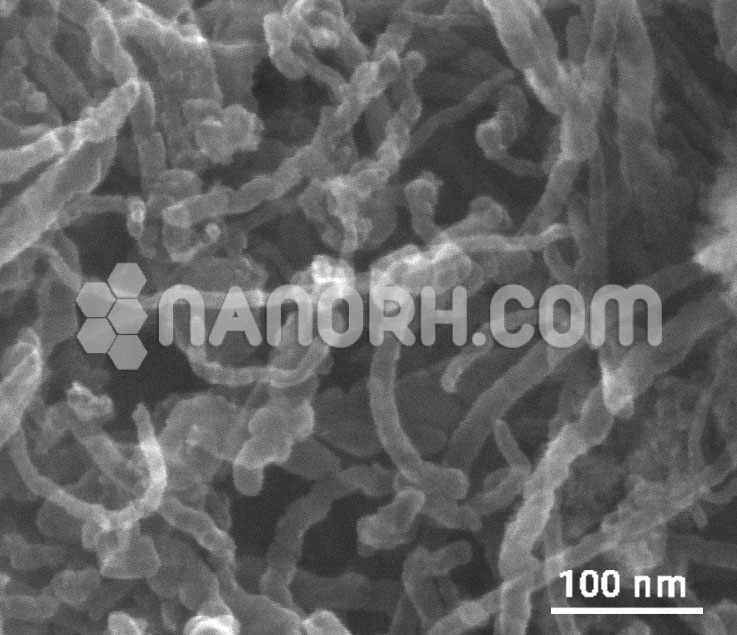
Graphene Nanoplatelets Water Dispersion
Introduction
Graphene Nanoplatelets water dispersion are thin, flat sheets of graphene that are typically a few nanometers thick but can have lateral dimensions ranging from hundreds of nanometers to a few micrometers. Due to their remarkable mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and large surface area, GNPs have attracted considerable attention for a wide variety of applications. However, to fully harness these properties in practical applications, it’s often necessary to disperse GNPs in a liquid medium, with water being one of the most common and environmentally friendly solvents.
Applications
Water-Based Coatings and Paints
Enhanced Durability and Conductivity: GNPs dispersed in water are incorporated into water-based coatings and paints to enhance their mechanical strength, conductivity, and thermal stability. These coatings are widely used in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. The graphene particles provide corrosion resistance, making the coatings durable even in harsh environments.
Anti-Corrosion: Water-dispersed GNPs are used in anti-corrosion coatings for metals, such as steel, to prevent rust and degradation. The graphene nanoplatelets form a protective barrier that makes the surface more resistant to moisture and environmental factors, which is especially important in industries such as marine, oil and gas, and construction.
Composites and Nanocomposites
Polymer Reinforcement: One of the most significant uses of water-dispersed GNPs is in the development of high-performance polymer composites. GNPs are mixed into polymers to significantly improve their mechanical properties (such as tensile strength and impact resistance), thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity. These composites are used in applications ranging from automotive parts to sports equipment and electronics.
Thermal Management: GNPs dispersed in water-based solutions can be used to enhance the thermal conductivity of composites. For example, GNPs can be incorporated into thermal interface materials (TIMs) used for heat dissipation in electronic devices like computers, LED lights, and smartphones.
Conductive Inks: In printed electronics, water-dispersed GNPs are used to create conductive inks for flexible circuits, RFID tags, and smart packaging. These inks allow for the printing of electronic circuits on a variety of substrates, including paper, plastic, and textiles, which is key for applications like wearable electronics and environmental sensors.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Supercapacitors: GNPs dispersed in water are utilized in supercapacitors to enhance the energy storage capacity and charge/discharge rates. The high surface area of GNPs allows for more efficient charge storage, which improves the performance of energy storage devices in terms of power density and cycle life.
Batteries: Water-dispersed GNPs are incorporated into electrodes of lithium-ion batteries to improve their electrical conductivity and cycling stability. The graphene nanoplatelets enhance the conductivity of the electrodes, leading to faster charge/discharge cycles and longer battery life.
Hydrogen Storage: Graphene nanoplatelets dispersed in water can also improve the performance of hydrogen storage systems. The high surface area of GNPs allows for the efficient adsorption of hydrogen molecules, which is critical for the development of hydrogen fuel cells and clean energy solutions.
Water Filtration and Purification
Graphene-based Membranes: GNPs are used to create graphene oxide membranes for water filtration and desalination. The high porosity and surface area of GNPs allow them to effectively filter out contaminants, including salts, organic molecules, and heavy metals. This makes them ideal for clean water production, wastewater treatment, and industrial water purification.
Pollutant Removal: Water-dispersed GNPs are also used in the removal of organic pollutants, dyes, and heavy metals from wastewater. GNPs can adsorb these harmful substances due to their high surface area, and their use in environmental remediation can help reduce pollution in water bodies and improve water quality.
Biomedical and Healthcare Applications
Drug Delivery Systems: Water-dispersed GNPs are being explored for their ability to deliver drugs more efficiently. The high surface area of GNPs allows for the attachment of a large number of drug molecules, which can be delivered to specific target areas in the body, improving the effectiveness of treatments, particularly in cancer therapy.
Biosensors: Water-dispersed GNPs are used in the development of biosensors for detecting specific biomolecules, pathogens, or diseases. The large surface area of the graphene platelets allows for high sensitivity, which is beneficial for applications in diagnostics and medical monitoring.
Tissue Engineering: GNPs dispersed in water-based solutions can be integrated into scaffolds for tissue engineering. These scaffolds provide structural support to grow cells for regenerative medicine and implantable devices.