| Lead Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5126 |
| CAS | 7783-46-2 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | PbF2 |
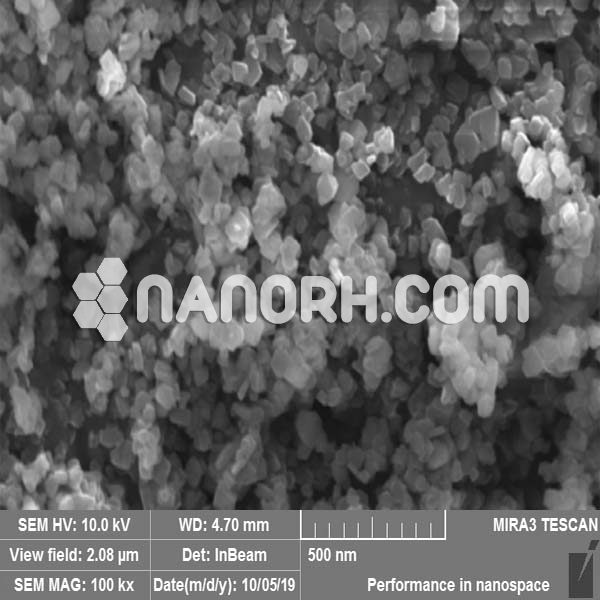
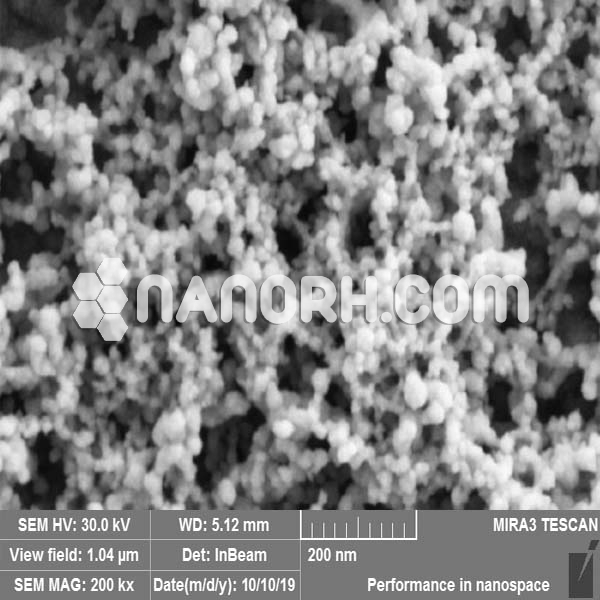
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Color | white |
| Molecular Weight | 245.20 g/mol |
| Density | 8.445 g/mL |
| Melting Point | 824 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1,293 °C |
Lead Fluoride Nanoparticles
Introduction
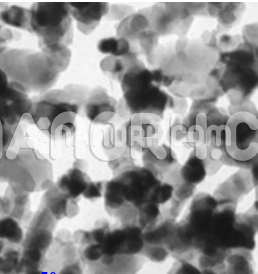
Lead fluoride (PbF₂) is an inorganic compound that consists of lead (Pb²⁺) and fluoride (F⁻) ions. It is a white crystalline solid with a high melting point (around 1270°C) and exhibits good chemical stability and high solubility in water. When reduced to the nanoscale, PbF₂ nanoparticles undergo significant changes in their physical and chemical properties due to the increased surface area and quantum effects.
Properties
Quantum Size Effects:
PbF₂ nanoparticles exhibit quantum confinement effects, which alter their electronic and optical properties compared to their bulk counterpart. As the particle size decreases, the band gap increases, which can lead to changes in absorption and emission spectra, offering unique opportunities in optical devices and sensing.
Optical Properties:
PbF₂ nanoparticles are known for their high transparency in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible regions, which makes them valuable in optical and photonics applications. Their ability to absorb and emit light at different wavelengths is particularly beneficial in fluorescence and luminescence-based technologies.
High Chemical and Thermal Stability:
PbF₂ exhibits remarkable thermal stability, making PbF₂ nanoparticles suitable for applications in high-temperature environments. Their chemical stability also allows them to be used in harsh chemical environments, which is beneficial in fields like catalysis and environmental sensing.
Fluorescent Properties:
PbF₂ nanoparticles, particularly when doped with rare-earth elements such as europium (Eu³⁺) or terbium (Tb³⁺), can exhibit strong fluorescent properties. This makes them useful in biomedical imaging and optical sensing applications.
High Surface Area:
At the nanoscale, PbF₂ nanoparticles have a significantly increased surface area, which enhances their reactivity and makes them effective in catalysis, adsorption, and sensor applications.