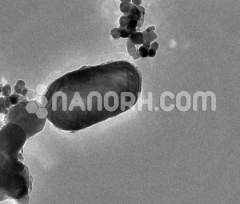
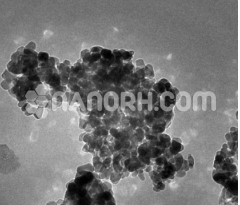
Magnesium Fluoride Pellets
Magnesium Fluoride Pellets
| Magnesium Fluoride Pellets | |
| Product No | NRE-52082 |
| CAS No. | 7783-40-6 |
| Formula | MgF2 |
| Molecular Weight | 62.3 g/mol |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Density | 5.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1260 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2,260° C |
| Shape | Pellet |
| Electrical Resistivity | NA |
| Electronegativity | NA |
Magnesium Fluoride Pellets
Magnesium fluoride (MgF₂) pellets are utilized in several high-tech and industrial applications due to their unique properties, such as high optical transparency, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Here’s a detailed overview of the primary applications for magnesium fluoride pellets:
Optical Coatings
Anti-Reflective Coatings: Magnesium fluoride is widely used in anti-reflective coatings for optical lenses, such as those found in cameras, microscopes, and binoculars. Its low refractive index helps reduce reflections and improve light transmission, enhancing the quality of optical devices.
Protective Coatings: MgF₂ coatings are applied to optical elements to protect them from scratches, environmental damage, and contaminants. This helps in maintaining the performance and longevity of optical components.
Laser Technology
Laser Optics: Magnesium fluoride is used in the production of optical elements for lasers, including lenses, windows, and prisms. Its high damage threshold and optical clarity make it suitable for high-power laser applications.
UV Laser Windows: MgF₂ is particularly effective in ultraviolet (UV) laser systems due to its excellent transmission properties in the UV range. It is used in UV laser windows and lenses to ensure efficient operation.
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Applications
Spectroscopy: Magnesium fluoride pellets are used in spectroscopy, particularly in instruments that analyze UV and visible light. The material’s optical properties contribute to accurate measurements and analysis.
Electronics and Semiconductors
Dielectric Material: MgF₂ can be used as a dielectric material in certain electronic and semiconductor applications. Its electrical insulating properties make it suitable for use in specific high-frequency and high-voltage applications.
High-Energy Physics
Detector Windows: In high-energy physics experiments, magnesium fluoride is used as a window material for radiation detectors. Its ability to withstand high-energy radiation while maintaining optical clarity makes it valuable for this purpose.
Infrared Applications
Infrared Optics: Although less common than its use in UV and visible ranges, MgF₂ can also be used in infrared optical applications. Its transmission properties in specific infrared wavelengths make it suitable for certain IR optical systems.
Optical Instruments
Precision Instruments: MgF₂ is used in precision optical instruments and systems where high optical performance and durability are required. This includes devices like interferometers and photometers.
Research and Development
Material Science: Magnesium fluoride pellets are used in research to explore new materials and technologies. Researchers study MgF₂ for its optical, chemical, and physical properties to develop advanced materials for various applications.