Metal Nanopowder 100nm 99.95% (Platinum, Rhodium,Palladium, Ruthenium, Iridium, Gold)
Metal Nanopowder
| Metal Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-1000 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Formula | NA |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | NA |
| Molecular Weight | NA |
| Density | NA |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Metal Nanopowder
Introduction
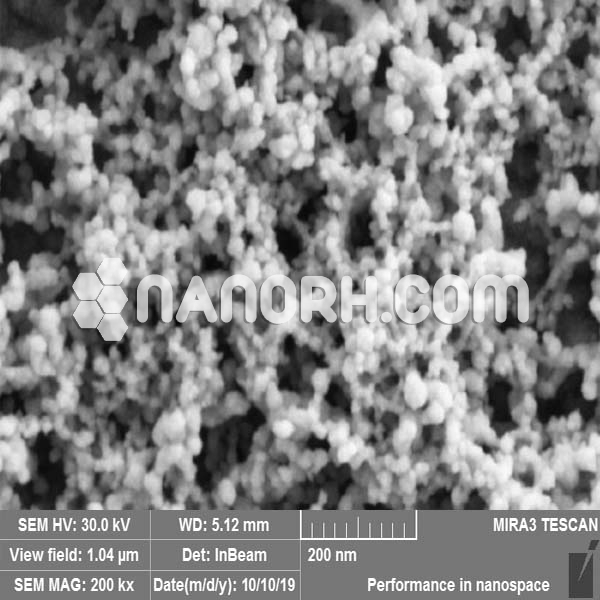
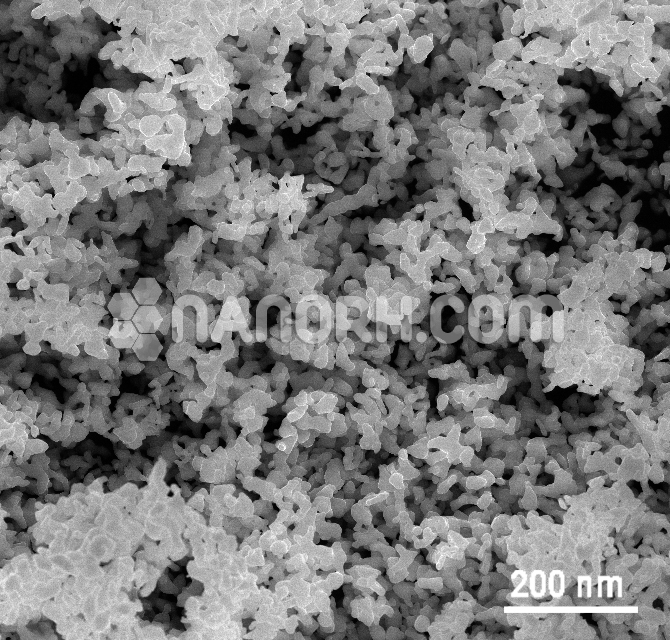
Metal nanopowder refer to fine powders composed of metallic particles with sizes typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers. At the nanoscale, metals exhibit distinct and enhanced properties compared to their bulk counterparts, such as improved strength, reactivity, conductivity, and catalytic activity. These unique characteristics arise primarily from the increased surface-to-volume ratio and quantum effects at the nanoscale, making metal nanopowders useful in a wide range of applications across various industries.
Properties of Metal Nanopowders
High Surface Area: Metal nanoparticles have a significantly higher surface area compared to their bulk counterparts. This increases their reactivity and makes them ideal for use in applications such as catalysis and sensing.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Many metal nanopowders, such as gold and silver, retain excellent electrical and thermal conductivity at the nanoscale. This makes them useful in electronic, energy, and cooling applications.
Magnetic Properties: Some metal nanopowders, like iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni), exhibit magnetic properties at the nanoscale. This enables their use in magnetic applications, such as data storage, sensors, and medical imaging.
Enhanced Chemical Reactivity: Metal nanopowders, due to their high surface area and increased reactivity, are widely used as catalysts in various chemical reactions.
Mechanical Strength: Metal nanopowders can offer enhanced mechanical properties such as strength, hardness, and flexibility. When incorporated into composites, they can enhance the properties of materials, making them stronger, lighter, and more durable.