| Molybdenum Telluride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5167 |
| CAS No. | 12058-20-7 |
| Formula | MoTe2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | NA |
| Molecular Weight | 351.14 g/mol |
| Density | 7.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
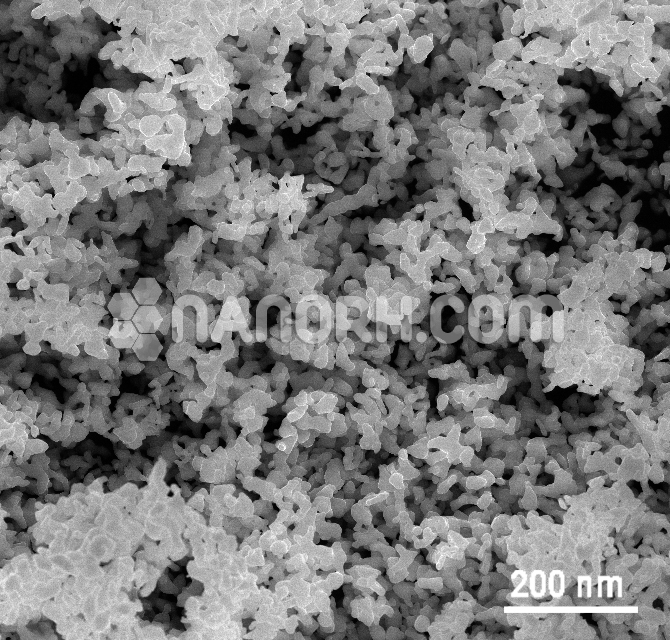
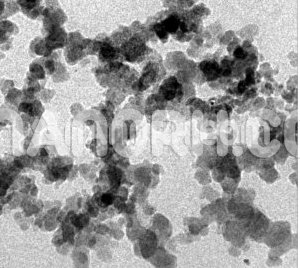
Molybdenum Telluride Nanoparticles
Molybdenum telluride nanoparticles are part of a group of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), which are known for their unique properties, including a range of electronic, optical, and catalytic behaviors. MoTe₂, in particular, has attracted significant interest due to its excellent electrical conductivity, thermoelectric properties, and potential for use in various advanced technologies. In nanoparticle form, these materials exhibit enhanced reactivity, larger surface areas, and novel physical properties that make them suitable for a variety of applications across energy storage, catalysis, electronics, and more.
Applications of Molybdenum Telluride Nanoparticles
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Lithium-Ion and Sodium-Ion Batteries: MoTe₂ nanoparticles are being explored as anode materials for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. Their high capacity and good cycling stability make them promising candidates for next-generation energy storage devices. MoTe₂’s layered structure allows for efficient ion intercalation, which enhances battery performance.
Supercapacitors: MoTe₂ nanoparticles are studied for use in supercapacitors, where their high surface area and excellent electrical conductivity enable fast charge/discharge cycles and high power density. These properties are essential for devices that require rapid energy release, such as electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Thermoelectric Devices: MoTe₂ has a relatively high thermoelectric figure of merit due to its low thermal conductivity and good electrical conductivity, making it useful in thermoelectric applications. Nanostructured MoTe₂ can be used in devices that convert heat into electricity, such as power generation systems or waste-heat recovery systems.