| Niobium Boride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5176 |
| CAS No. | 12007-29-3 |
| Formula | NbB2 |
| Density | 6.97 g/cm3 |
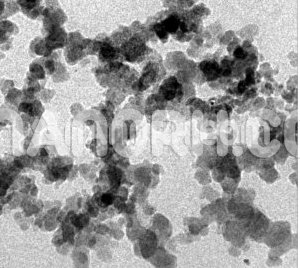
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Form | Powder |
| Molecular Weight | 114.528 g/mol |
| Certificate Of Analysis | |
| Nb | 81.1% |
| B | 18.8% |
| S | 0.02% |
| Mn | 0.03% |
| W | 0.02% |
| Cr | 0.01% |
| Ti | 0.01% |
Niobium Boride Nanoparticles
Introduction
Niobium boride nanoparticles is a highly interesting and valuable compound composed of niobium (Nb) and boron (B) atoms. When reduced to the nanoparticle scale, niobium boride nanoparticles possess unique properties that make them useful in various advanced technological and industrial applications.
Niobium is a transition metal known for its high melting point, corrosion resistance, and strong bonding with boron, which imparts several desirable properties to NbB, including hardness, high thermal stability, and excellent electrical conductivity.
Properties
High Hardness: NbB2 are extremely hard, which makes them useful in wear-resistant materials and cutting tools.
Thermal Stability: These nanoparticles have excellent thermal stability, even at elevated temperatures, which is advantageous in high-temperature applications.
Electrical Conductivity: NbB has high electrical conductivity, which makes it useful in electronics and other fields requiring efficient conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance: The compound is resistant to corrosion, adding durability and longevity to materials in harsh environments.
Mechanical Strength: Niobium boride exhibits superior mechanical strength, enhancing its role in composite materials and coatings.
Synthesis
Niobium boride nanoparticles are typically synthesized using methods such as:
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A common technique to produce high-quality NbB nanoparticles with controlled morphology and uniformity.
Sol-Gel Method: A relatively low-temperature approach that involves creating a gel-like substance and converting it into nanoparticles upon heating.
Mechanical Milling: A method where bulk niobium boride is subjected to grinding, resulting in the formation.