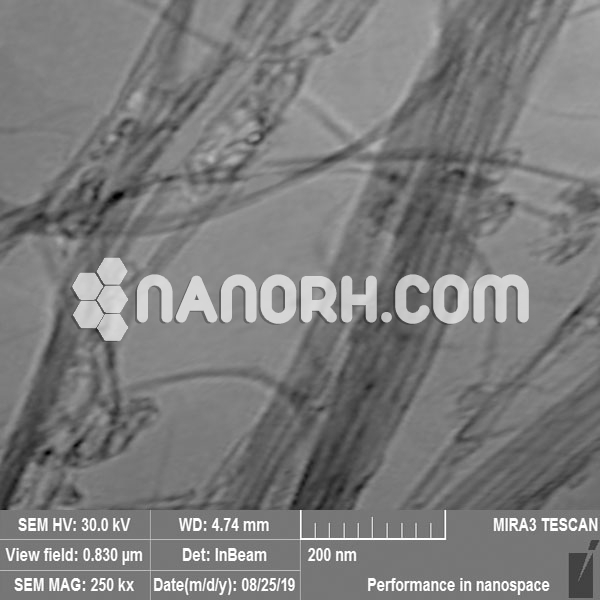
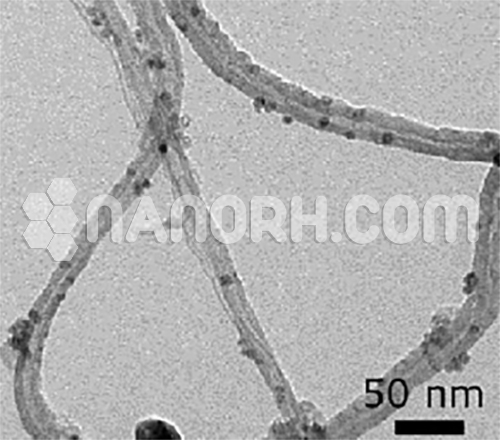
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Fullerenols) / C60, -OH Functionalized
The starting material is >99% purity C60 fullerenes. C60 bearing over 40 hydroxyl groups that have higher water solubility (>50 mg/mL).
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Fullerenols) / C60, -OH Functionalized
| Product No | NRE-41008 |
| CAS | 99685-96-8 |
| Purity | >99% |
| Melting Point | >280 °C |
| Morphology | Spherical |
| Flash Point | > 94 °C |
| Density | 1.6 g/cm³ at 20 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C60 |
| Molecular Weight | 720.64 g/mol |
| Form | Crystalline powder |
| Orbital energy | HOMO 6.1-6.2 eV |
| Orbital energy | UMO 4.5 eV |
| Reactivity | Non Reactive/ Non Soluble |
| Stability | Completely Stable |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents |
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Research Grade Fullerenols):
Polyhydroxylated fullerenes, commonly known as fullerenols, are derivatives of fullerene molecules (such as C₆₀, C₇₀, or other larger fullerenes) that have been chemically modified by the attachment of hydroxyl groups (-OH) to their surface.
Applications:
Polyhydroxylated fullerenes (fullerenols) are gaining significant attention due to their diverse properties and wide range of applications, particularly in biomedicine, nanotechnology, and environmental science. Below are some of the primary areas where fullerenols are being researched and applied.
Biomedical Applications
Drug Delivery Systems:
Fullerenols are used in the development of drug delivery systems due to their water solubility, biocompatibility, and ability to encapsulate drugs. The hydroxyl groups on the fullerene surface can serve as binding sites for drug molecules, improving the solubility and controlled release of drugs. This is particularly important for drugs with low water solubility, as fullerenols can improve their bioavailability.
Antioxidant Therapy:
Fullerenols exhibit strong antioxidant properties, making them suitable candidates for treating oxidative stress-related diseases such as neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes. Their ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) can help mitigate damage caused by oxidative stress, which is implicated in aging and various chronic diseases.
Gene Delivery:
Fullerenols can be used as vectors for gene delivery or gene therapy. Due to their biocompatibility, solubility, and surface reactivity, they can encapsulate DNA or RNA and deliver them to specific cells for gene editing or gene silencing applications. Fullerenols can be functionalized with targeting ligands for site-specific delivery to cancer cells or other diseased tissues.
Biosensing and Diagnostic Applications:
Fullerenols are being developed for use in biosensors for detecting biological markers or environmental toxins. Their ability to bind to biomolecules and change their properties makes them ideal for diagnostic applications. They can be functionalized with specific ligands or used as fluorescent probes for detecting diseases at an early stage.
Nanotechnology and Materials Science
Nanocomposites and Coatings:
Fullerenols are incorporated into nanocomposite materials to enhance their mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. These materials can be used in electronics, solar cells, and lightweight materials. Fullerenols can improve the strength and stability of composites when integrated with polymers, metals, or ceramics.