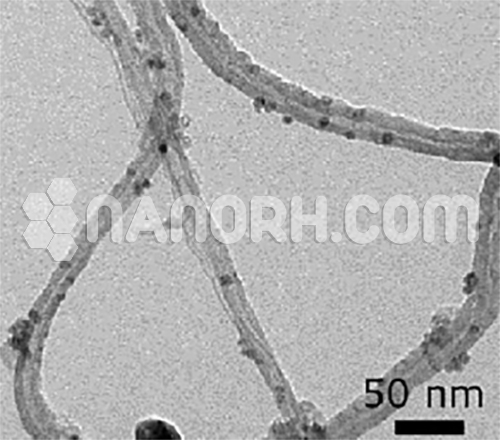
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Fullerenols) / C60, -OH Functionalized
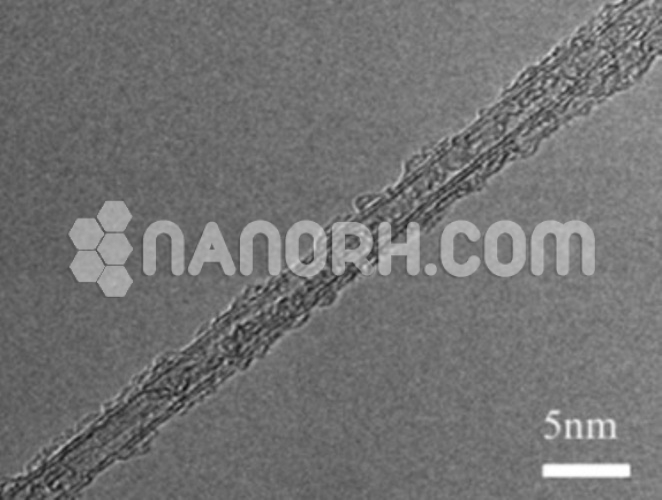
The starting material is >99% purity C60 fullerenes. C60 bearing over 40 hydroxyl groups that have higher water solubility (>50 mg/mL).
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Fullerenols) / C60, -OH Functionalized
| Product No | NRE-41009 |
| CAS | 99685-96-8 |
| Purity | >99.9% |
| Melting Point | >280 °C |
| Morphology | Spherical |
| Flash Point | > 94 °C |
| Density | 1.6 g/cm³ at 20 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C60 |
| Molecular Weight | 720.64 g/mol |
| Form | Crystalline powder |
| Orbital energy | HOMO 6.1-6.2 eV |
| Orbital energy | UMO 4.5 eV |
| Reactivity | Non Reactive/ Non Soluble |
| Stability | Completely Stable |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents |
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Research Grade Fullerenols): The starting material is >99% purity C60 fullerenes. C60 bearing over 40 hydroxyl groups that have higher water solubility (>50 mg/mL). These exist as monodisperse nanoparticles in water and have a valiant polishing effect. They exhibit superior antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties
Applications
Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications
Drug Delivery Systems:
Fullerenols can serve as drug carriers or nanocarriers due to their water solubility and ability to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs. The hydroxyl groups on the fullerene surface allow them to bind to and release therapeutic agents in a controlled manner. Fullerenols can be used to improve the bioavailability and targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs, antibiotics, and other pharmaceuticals.
Gene Delivery:
Fullerenols are being researched as vectors for gene delivery. Their surface chemistry allows them to carry nucleic acids (such as DNA or RNA) and deliver them into specific cells or tissues, making them candidates for gene therapy applications. By functionalizing fullerenols with specific targeting ligands, gene delivery can be more selective and efficient.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Therapy:
Due to their antioxidant properties, fullerenols are being studied as therapeutic agents for treating diseases related to oxidative stress, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes. Their ability to neutralize free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) helps mitigate cellular damage caused by these molecules.
Biosensing and Diagnostic Applications:
Fullerenols can be used in the development of biosensors for detecting biomolecules or pathogens. Their fluorescent properties and surface reactivity allow them to be functionalized with specific biorecognition elements, making them useful for detecting diseases, toxins, and biomarkers in medical diagnostics.
Environmental Applications
Water Purification:
Fullerenols have been explored for their ability to remove toxic chemicals from water. The hydrophilic nature of fullerenols enables them to interact with and adsorb pollutants, including heavy metals, organic contaminants, and pesticides. This makes fullerenols useful for water treatment and pollution remediation.