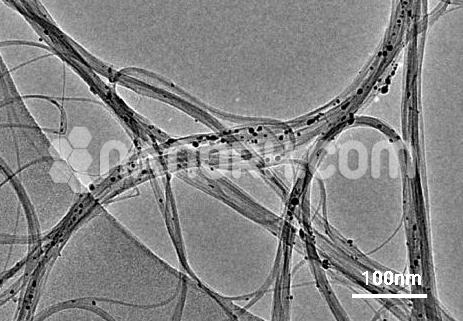
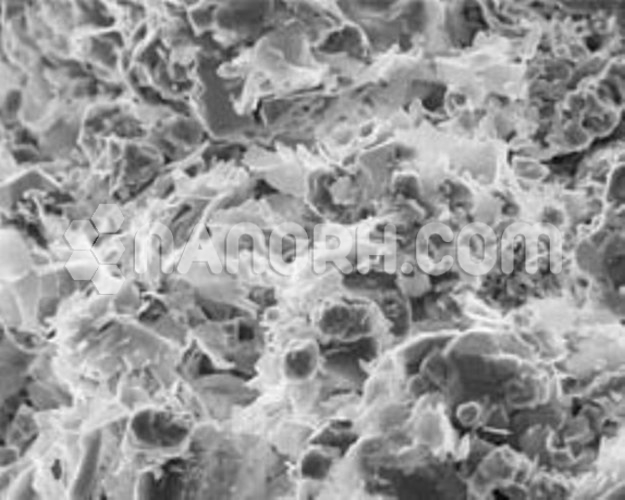
Research Grade Single Layer Graphene Oxide Water Dispersion (Thickness 0.43 – 1.23 nm, Diameter 1.5 – 5.5 um, Dispersed in water with 2wt%)
| Research Grade Single Layer Graphene Oxide Water Dispersion | |
| Product No | NRE-39026 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Molecular Weight | 1.5-5.5 μm |
| APS | NA |
| Purity | >99.3wt% |
| Color | NA |
| Density | NA |
| Electric Conductivity | NA |
Research Grade Single Layer Graphene Oxide Water Dispersion
Introduction
Research grade Single layer graphene oxide water dispersion is a highly oxygenated form of graphene, which contains epoxide, hydroxyl, and carboxyl groups on its surface, making it hydrophilic and highly dispersible in water. Research-grade single-layer graphene oxide water dispersion refers to a stable, aqueous suspension of graphene oxide nanoparticles that are dispersed and stabilized in water, typically with the aid of surfactants or functionalization to prevent agglomeration.
Applications
Composite Materials
Polymer Nanocomposites: The dispersion of single-layer graphene oxide in water is often used to create graphene oxide-based polymer nanocomposites. These composites benefit from the mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical properties of graphene oxide. The dispersed state in water allows for easier mixing and incorporation into various polymers (such as epoxy, polyethylene, or polymers of intrinsic conductivity), enhancing their properties for use in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and sports equipment industries.
Conductive Films: The water dispersion of graphene oxide is used to form conductive thin films by coating substrates. After reduction (partially or fully), these films can be used in electronics (such as touchscreens, displays, and solar cells), and flexible electronics where high electrical conductivity and flexibility are needed.
Thermal Management Composites: The dispersion of graphene oxide in water allows for easier integration into composite materials for thermal management in devices such as heat sinks or thermal interface materials (TIMs). The high thermal conductivity of graphene oxide enhances the ability of composites to dissipate heat, especially in electronics and high-power systems.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Supercapacitors: The aqueous dispersion of graphene oxide is used in the development of supercapacitors. The oxygenated functional groups on graphene oxide can improve the ionic conductivity of supercapacitor electrodes and increase the surface area for charge storage. In this application, graphene oxide can be reduced to form high-capacity and high-efficiency supercapacitor electrodes for applications in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and emergency power supply.