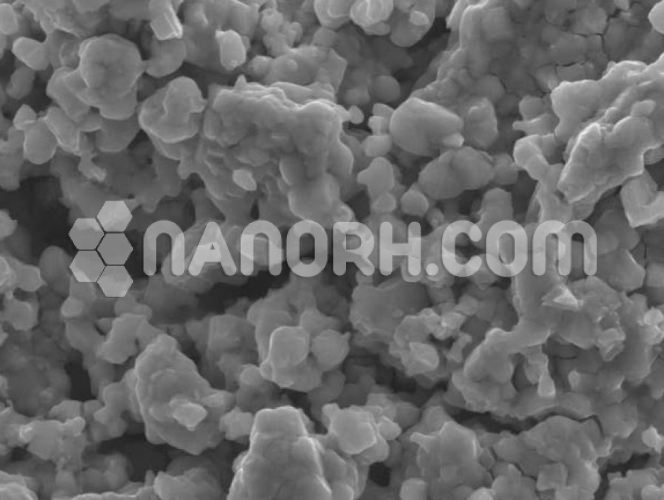
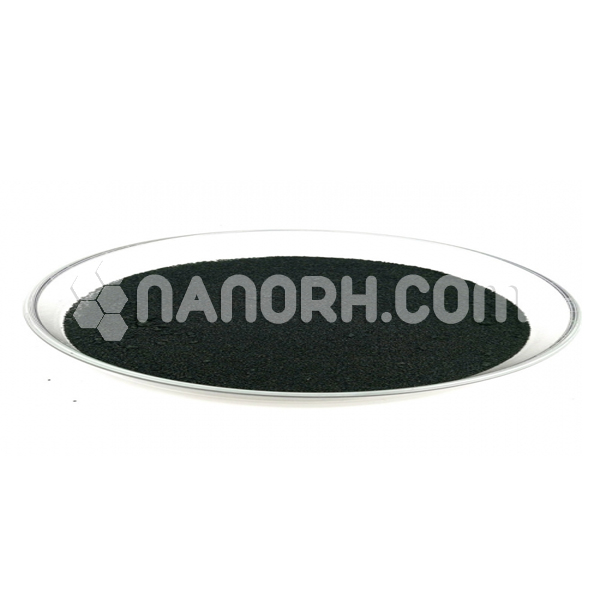
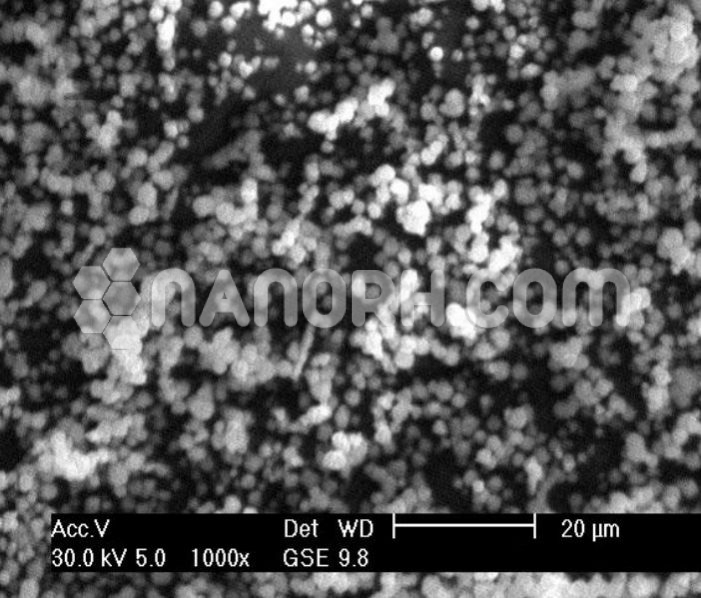
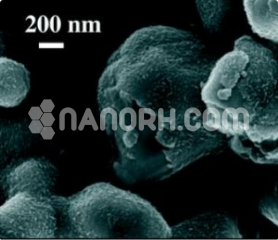
| Rhodium Metal Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-25010 |
| CAS | 7440-16-6 |
| Purity | 99.9 % |
| Molecular Formula | Rh |
| Molecular Weight | 102.91 g/mol |
| Color | Gray |
| Density | 12.41 g/cm³ |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 1966 °C |
| Boiling Point | 3968 °C |
Rhodium Metal Nanoparticles
Rhodium (Rh) metal nanoparticles are known for their unique physical and chemical properties, which make them valuable in a variety of advanced applications. Here are some notable applications for rhodium metal nanoparticles:
Catalysis: Rhodium nanoparticles are extensively used as catalysts in a range of chemical reactions. They are particularly valuable in:
Hydrogenation Reactions: Used for the hydrogenation of alkenes, alkynes, and other organic compounds.
Catalytic Converters: Essential in automotive catalytic converters to reduce harmful emissions, including the oxidation of carbon monoxide and the reduction of nitrogen oxides.
Organic Synthesis: Employed in various organic synthesis processes, including hydroformylation and other reactions.
Electrochemical Applications: Rhodium nanoparticles are used in electrochemical applications, such as:
Fuel Cells: As electrocatalysts in fuel cells, rhodium can improve the efficiency of the electrochemical reactions.
Batteries: Used in the development of advanced battery systems to enhance performance and longevity.
Sensors: Rhodium nanoparticles are employed in the development of chemical and gas sensors due to their high catalytic activity and sensitivity. They can detect gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other substances.
Optoelectronics: Rhodium nanoparticles can be used in optoelectronic devices. Their ability to interact with light and their unique electronic properties can be harnessed in applications such as:
Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS): Enhances the Raman signal of molecules, making it useful for sensitive detection and analysis.
Photodetectors: Utilized in devices that detect and measure light.
Biomedical Applications: The biocompatibility of rhodium nanoparticles makes them suitable for various biomedical applications, including:
Imaging: Used as contrast agents in imaging techniques like X-ray and MRI.
Therapeutics: Investigated for potential use in targeted drug delivery and cancer treatment due to their ability to generate heat upon irradiation (photothermal therapy).
Material Science: Rhodium nanoparticles are incorporated into materials to enhance their properties, such as:
Alloys and Composites: Used to strengthen or modify the properties of alloys and composites in advanced materials.
Thin Films: Employed in thin films for electronic and optical devices.
Environmental Applications: Rhodium nanoparticles are used in environmental applications such as:
Pollutant Removal: Catalyzing the breakdown of pollutants or hazardous substances in wastewater treatment and air purification.