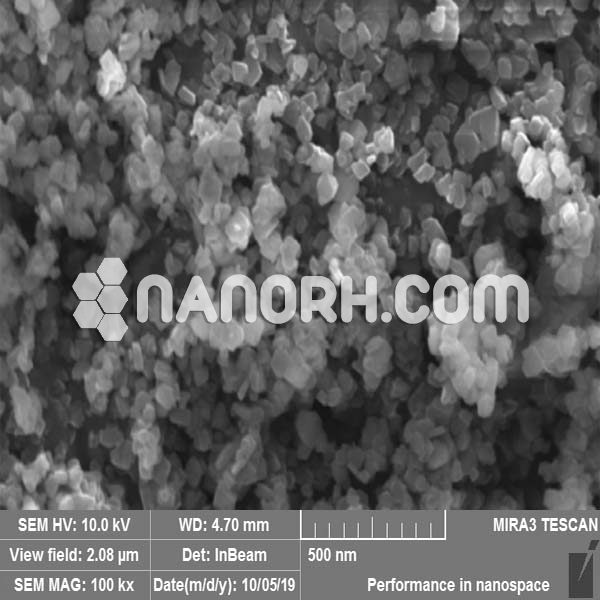
| Tin Iodide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-5229 |
| CAS | 10294-70-9 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Formula | SnI2 |
| Molecular Weight | 372.52 g/mol |
| Color | red to red-orange |
| Density | 7.6 g/cm3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 320° C |
| Boiling Point | 714° C |
Tin Iodide Nanopowder
Applications
Photovoltaic and Solar Cells:
Thin-Film Solar Cells: SnI₂ is being explored as a potential material for use in thin-film solar cells due to its narrow bandgap and high absorption efficiency in the visible spectrum. It can be used as a light-absorbing layer to convert sunlight into electrical energy.
Perovskite Solar Cells: Tin iodide plays a role in perovskite-based solar cells as it can help in the formation of Sn-based perovskites that have excellent photovoltaic properties and high efficiency.
Energy Storage:
Battery Technology: Tin iodide nanopowder can be used in lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. The material enhances the charge/discharge capacity and cycle stability of energy storage systems due to its high surface area and chemical reactivity.
Electrode Materials: SnI₂ can be used in the anodes of batteries, where its excellent ionic conductivity and charge storage ability improve battery performance.
Optoelectronics:
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): SnI₂ nanoparticles are employed in LEDs due to their light-emitting properties when excited by an electric current. They can be used in display technology and lighting applications.
Photodetectors: SnI₂ is also used in photodetectors for optical communication systems and imaging applications. The material is sensitive to light and can convert light into an electrical signal, making it useful for optical sensors.
Catalysis:
Chemical Catalysis: Due to its high surface area, SnI₂ nanopowder is used as a catalyst in various chemical reactions, such as oxidation and reduction processes. It can accelerate reactions in organic synthesis and help in hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions.
Environmental Catalysis: SnI₂ is being explored for applications in environmental remediation, such as pollution control, by aiding in the decomposition of pollutants in the air or water.