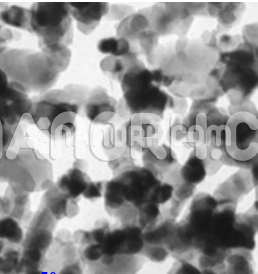
| Copper Iodide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5070 |
| CAS | 7681-65-4 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Formula | CuI |
| Molecular Weight | 190.45 g/mol |
| Color | White |
| Density | 5.67 g/cm3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 606° C |
| Boiling Point | 1,290° C |
Copper Iodide Nanoparticles
Optoelectronics and Photonics:
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): CuI nanoparticles are used in LEDs, where their excellent optoelectronic properties, such as high luminescence efficiency, allow for efficient light emission, particularly in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible spectra.
Photodetectors: CuI nanoparticles can be used in photodetectors, which are devices that detect light and convert it into an electrical signal. Their ability to absorb light in the UV to visible range makes them suitable for solar cells and light-sensing applications.
Solar Cells: CuI is being studied as a material for solar cells, particularly for thin-film photovoltaics. CuI’s semiconductor properties, coupled with its relatively low cost, make it a promising material for next-generation solar energy devices.
Catalysis:
Catalysis in Organic Reactions: CuI nanoparticles have been shown to be effective catalysts in a variety of organic reactions, such as the oxidation of alcohols, coupling reactions, and carbon-carbon bond formations. These catalytic properties make CuI nanoparticles useful in industrial chemical synthesis.
Hydrogenation Reactions: CuI nanoparticles are also used in hydrogenation processes, which are important in the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Environmental Catalysis: CuI nanoparticles can be used in the degradation of organic pollutants in water and air. Their photocatalytic properties allow them to break down harmful substances under UV or visible light exposure, making them valuable in environmental remediation.
Environmental Remediation:
Water Purification: CuI nanoparticles can be employed in photocatalytic processes to remove pollutants from water. They are capable of breaking down organic contaminants like dyes, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals in water under UV or visible light, contributing to water purification efforts.
Air Purification: CuI’s photocatalytic activity extends to air purification applications, where these nanoparticles can help degrade volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other airborne pollutants under light exposure.
Sensing and Detection:
Gas Sensors: CuI nanoparticles are used in the design of sensors for detecting gases such as ammonia, nitrogen oxides, and carbon dioxide. Their high surface area and semiconducting properties make them ideal for sensitive detection of gases.