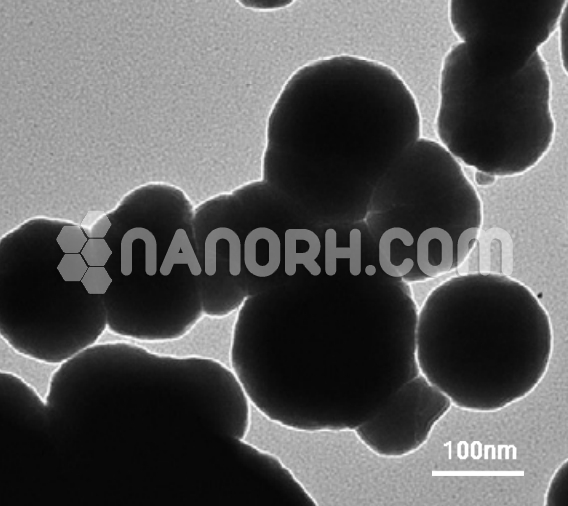
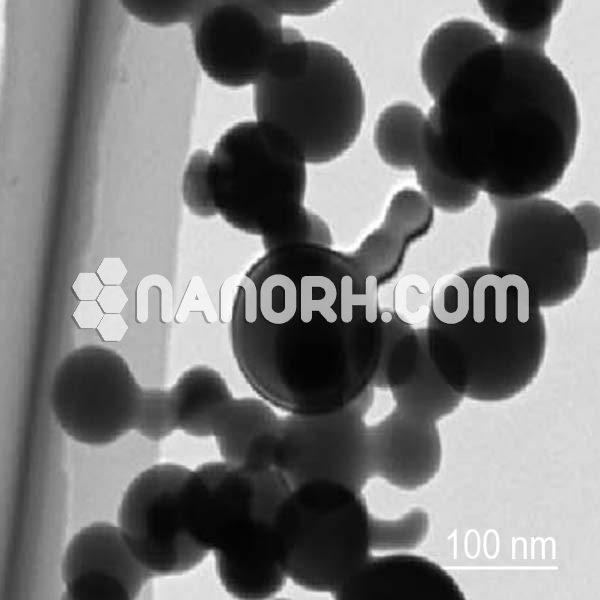
| Hagg Iron Carbide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-5116 |
| CAS No. | 7439-89-6/7440-44-0 |
| Formula | Fe5C2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | NA |
| Magnetization | 140 emu/g |
| Coercivity | 703 Oe |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Appearance | Powder |
Hagg Iron Carbide Nanopowder
Hagg iron carbide nanopowder also known as cementite or iron carbide (Fe₃C), is a chemical compound composed of iron and carbon. It plays a crucial role in the microstructure of steels and cast irons, contributing to their hardness, strength, and brittleness. When in the form of nanopowder, iron carbide (Fe₃C) exhibits unique properties that are not present in its bulk form, largely due to its small particle size, high surface area, and the ability to be integrated into nanocomposites for specialized applications.
The synthesis of Hagg iron carbide nanopowder can be achieved through various methods such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), laser ablation, ball milling, sol-gel processes, or hydrothermal synthesis, depending on the desired particle size, morphology, and material purity.
Applications
Materials Science and Engineering:
Wear-Resistant Coatings: Iron carbide nanopowders are ideal for use in wear-resistant coatings applied to machinery components, tools, and parts exposed to friction or abrasive environments. Examples include brake pads, cutting tools, engine parts, and high-performance bearings. These coatings improve the service life and efficiency of critical industrial equipment.
Hard Metal Alloys: The addition of Fe₃C nanopowder to metal alloys, particularly steel and cast iron, enhances strength, hardness, and wear resistance. The powder can be used in the fabrication of tool steels, high-carbon steels, and other hard metal alloys.
Sintered Materials: Iron carbide nanopowders are often incorporated into sintered metal products, which are widely used in the manufacturing of gears, machine parts, and other heavy-duty components. The high hardness of the nanopowder enhances the overall durability of sintered materials.
Catalysis:
Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation Reactions: Iron carbide nanopowders are effective catalysts in chemical reactions like hydrogenation (adding hydrogen to organic compounds) and dehydrogenation (removing hydrogen from molecules). These reactions are important in the production of pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and biofuels.
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Fe₃C nanopowders are also used as catalysts or catalyst supports in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, a process where carbon monoxide and hydrogen are converted into liquid hydrocarbons. This process is important for fuel production and synthetic fuel technologies.