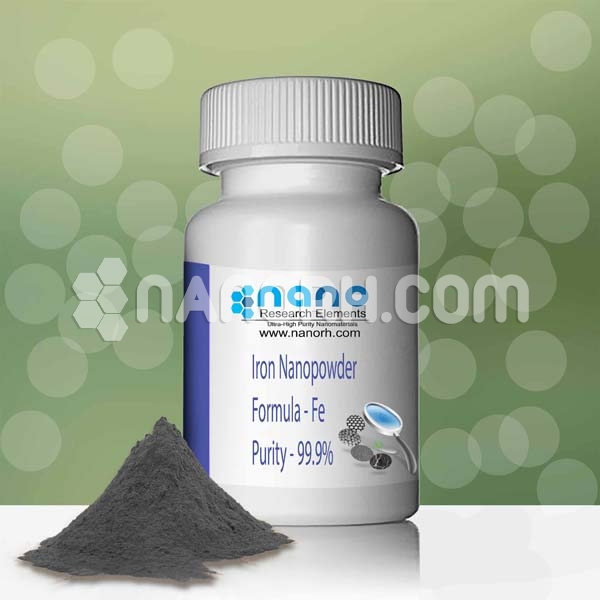
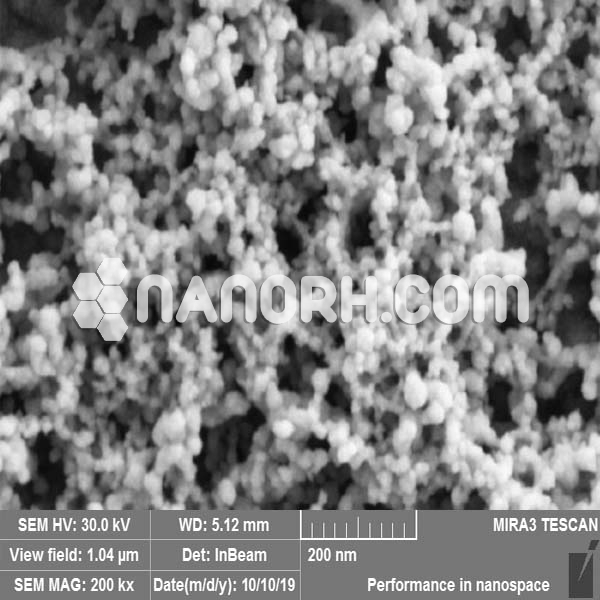
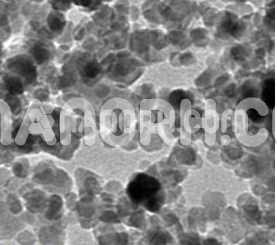
Iron Powder (Fe), 99%
Pure Iron Powder – Particle Shape is based on particle size–Making Method: Reduced Iron Powder
Mainly used for injection molding, magnetic materials and other industries..
| Iron Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-1021 |
| CAS No. | 7439-89-6 |
| Formula | Fe |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99% |
| Color | Dark Gray |
| Molecular Weight | 55.845 g/mol |
| Density | 7.874 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1538 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2862 °C |
Iron Powder – Particle Shape is based on particle size–Making Method: Reduced Iron Powder
Mainly used for injection molding, magnetic materials, and other industries.
Iron Powder – Particle Shape is based on particle size–Making Method: Carbonyl Iron Powder
Mainly used for powder metallurgy and injection molding, diamond tools, diamond catalyst, shielding materials, microwave absorbing materials…
Both two products Applications: Products are mainly used carbide, powder metallurgy, injection molding, welding materials, electronic materials, magnetic materials, diamond tools, rubber, plastic, etc
Iron Powder Applications
- Probing. Due to its sensitivity to magnetic fields, iron nanopowder plays a crucial role in the development of various tools for recording magnetic activity. It’s of particular interest for research projects analyzing fundamental magnetic interactions.
- Recording media. Basic magnetic data storage and high-density magnetic recording both benefit from the magnetic properties of iron nanopowders.
- Ferrofluids and pastes. In various electronic industrial applications, iron nanopowders can be utilized to produce effective ferrofluids, magnetic pastes, and similar compounds.
- Medical applications. A number of medical and biomedical applications for iron nanopowders have seen usage or extensive research in recent years. As with many other nanomaterials, its unique optical properties make it of interest in imaging solutions. It’s also seen use as a drug carrier for certain delivery mechanisms.
- Environmental applications. Iron nanopowders have shown promising results as a solution for certain forms of soil contamination, helping to degrade heavy metals and other compromising environmental hazards.
- Catalysts. A number of industries utilize iron nanopowder as a component in a catalyst, including metalworking and many others.
- Electromagnetic-wave absorption. The magnetic properties of iron nanopowder make it a viable material for the manufacture of electromagnetic shielding solutions, especially those where traditional options for electromagnetic wave absorption aren’t viable.