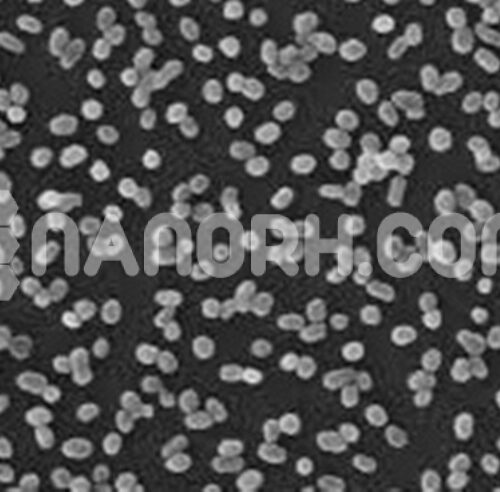
Lanthanum Hexaboride LaB6 Powder / LaB6 Lanthanum Boride Powder (High purity 99.9%, 1-20um)
Lanthanum Hexaboride Powder
| Lanthanum Hexaboride LaB6 Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-11141 |
| CAS No. | 12008-21-8 |
| Formula | LaB6 |
| Molecular Weight | 203.77 g/mol |
| APS | 1-20um(can be customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Density | 4.72g/cm3 |
| Color | Gray |
| Melting Point | 2210 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Lanthanum hexaboride LaB6 Powder
Lanthanum boride is a compound of lanthanum and boron. It is primarily used in powder form, and it has various applications due to its unique properties. Some of the common applications of lanthanum boride powder include:
Ceramic Industry: Lanthanum boride powder can be used as an additive in ceramic materials, where it can enhance the mechanical and thermal properties of ceramics.
Coatings: Lanthanum boride powder can be used in the production of coatings for various applications, including high-temperature environments. These coatings can provide protection against wear, corrosion, and oxidation.
Additive Manufacturing: Lanthanum boride powder is sometimes utilized in the additive manufacturing industry to create high-strength components, particularly in the aerospace and automotive sectors.
Catalysts: Lanthanum boride powder can serve as a catalyst in some chemical processes, facilitating specific reactions and improving the efficiency of various industrial processes.
Thermal Barrier Coatings: Due to its high melting point and thermal stability, lanthanum boride powder can be used in the development of thermal barrier coatings that protect materials from high temperatures, particularly in the aerospace and gas turbine industries.
Research and Development: Lanthanum boride powder is also used in various research and development activities, especially in the field of materials science and engineering, to explore its unique properties and potential applications in different industries.