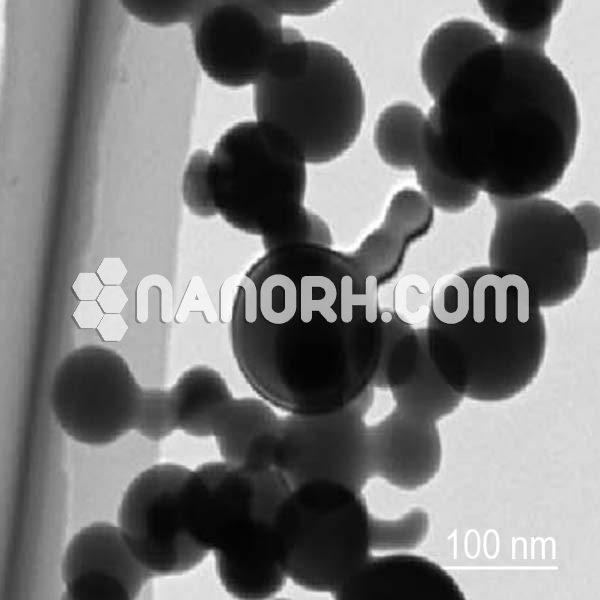
| Silicon Carbide Fine Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-5197 |
| CAS No. | 409-21-2 |
| Formula | SiC |
| APS | <1 µm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | bluish-black |
| Molecular Weight | 40.0962 g/mol |
| Density | 3.16 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 2830°C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Silicon Carbide Fine Powder
Silicon carbide fine powder is a compound made of silicon and carbon, known for its outstanding mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. When reduced to fine powder form, silicon carbide retains its characteristic hardness, chemical inertness, and high-temperature stability, making it highly versatile in various industrial applications. Silicon carbide is one of the hardest known materials, second only to diamond, which gives it exceptional wear resistance and strength. It is also a wide bandgap semiconductor, which allows it to be used in a variety of electronics and power devices, especially those requiring high efficiency and thermal conductivity.
Properties:
Hardness: Silicon carbide is one of the hardest materials known, with a Mohs hardness of 9-9.5, which makes it extremely resistant to wear and abrasion. This makes SiC fine powder suitable for use in abrasive applications.
High Thermal Conductivity: SiC has an excellent ability to conduct heat, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and heat sinks in electronic devices.
High Melting Point: With a melting point around 2,700°C, silicon carbide can withstand extreme heat without degrading. This makes it a key material for high-temperature applications.
Chemical Inertness: Silicon carbide is chemically stable and resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and most acids and alkalis, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
Electrical Conductivity: Silicon carbide exhibits a combination of semiconductor and insulator properties, depending on its purity and form. It can be used in power electronics for devices that need to operate at high voltages or frequencies.
High Strength and Toughness: Despite being brittle in its pure form, silicon carbide has high tensile strength and toughness, especially when used in composite materials.
Wide Bandgap: The wide bandgap of silicon carbide allows it to operate at higher voltages, frequencies, and temperatures than silicon-based devices, making it essential for high-power applications.