| Silver Copper Alloy Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-2042 |
| CAS No. | 12249-45-5 |
| Formula | Ag-Cu |
| Molecular Weight | 171.4142 g/mol |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Density | 9.7-10.4 g/cm3 |
| Color | Gray |
| Melting Point | 779-900 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Silver Copper Alloy Nanoparticles
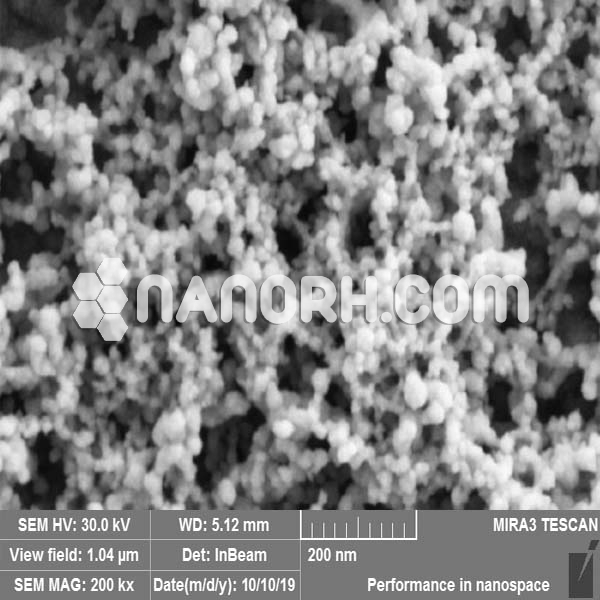
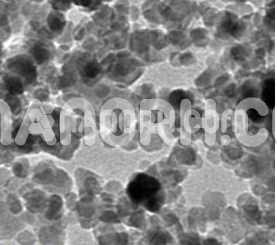
The current use of Ag-NP in the medical field is for the treatment of wounds, burns, disinfectants, and the development of orthopedic implants. Furthermore, Ag-NPs are extensively studied for their antimicrobial activity against a wide variety of bacteria. Furthermore, the antitumor activity of Ag-NP has been tested in different forms of cancer. Similarly, Cu-NP has been extensively studied for its antimicrobial activity, and recently the antiviral and antitumor activity of Cu-NP has also been reported. The synergistic effect of chitin-incorporated silver and copper nanoparticles showed greater toxicity in MCF-7 tumor cells than Ag-NP or Cu-NP; this suggests that the formation of the AgCu-NP alloy could be a potent anticancer agent for MCF-7 breast cancer. Based on the previous results of the anticancer properties of Ag-NP and Cu-NP, we aim to synthesize AgCu-NP alloy nanoparticles, which may exhibit synergistic modalities as a potent anticancer agent against cancer MCF-7. In this study, we aim to synthesize AgCu-NP as an anticancer agent and evaluate its cytotoxic effects on MCF-7 breast cancer. In this work Ag-NP, Cu-NP and three AgCu-NP alloys of different concentrations of silver and copper are chemically synthesized. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by their shape and size using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) and their hydrodynamic size and stability assessed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and zeta potential. Semi-quantitative chemical analysis of the nanoparticles was performed by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) to determine silver or copper and the ratio of silver and copper among the alloy nanoparticles. In addition, the toxicity in cells caused by the nanoparticles for the apoptotic pathway and the regulation of metalloprotease enzymes, which are crucial in the cell death pathway, were further evaluated. The possible mechanism of toxicity driven by Ag-NP or Cu-NP is mainly due to oxidative stress, damage to DNA and lipids by oxide.