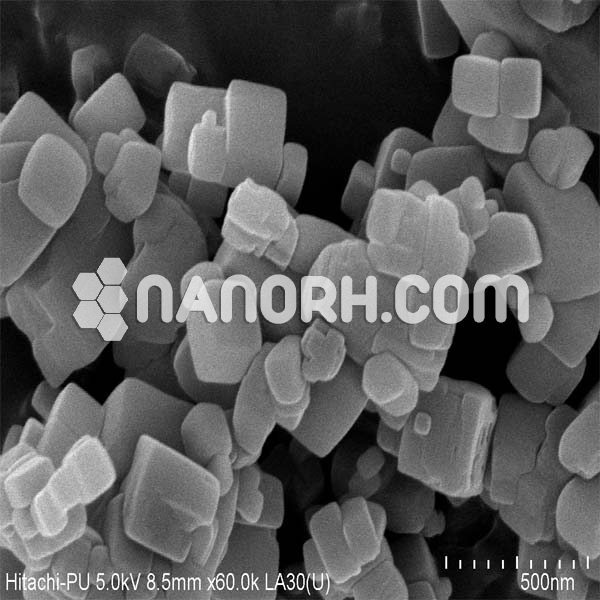
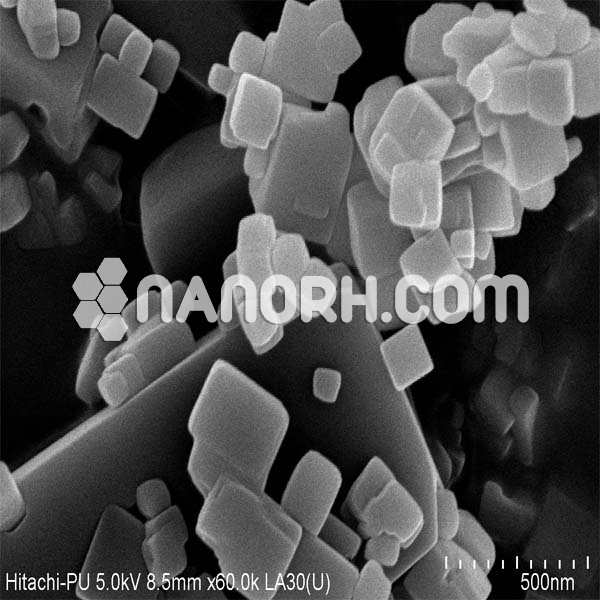
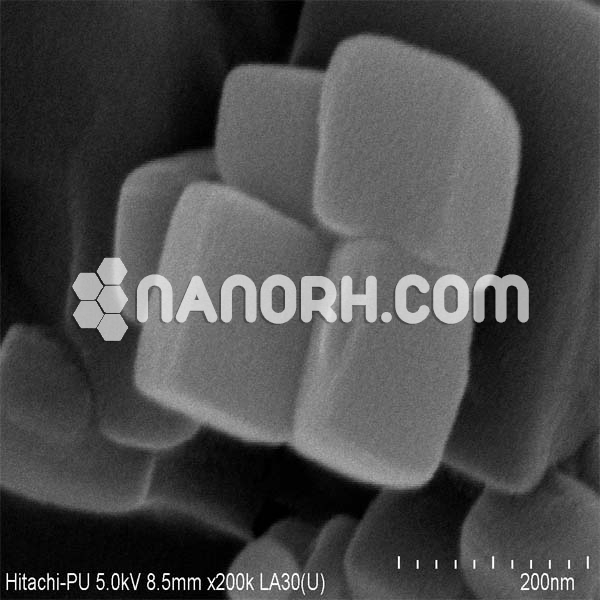
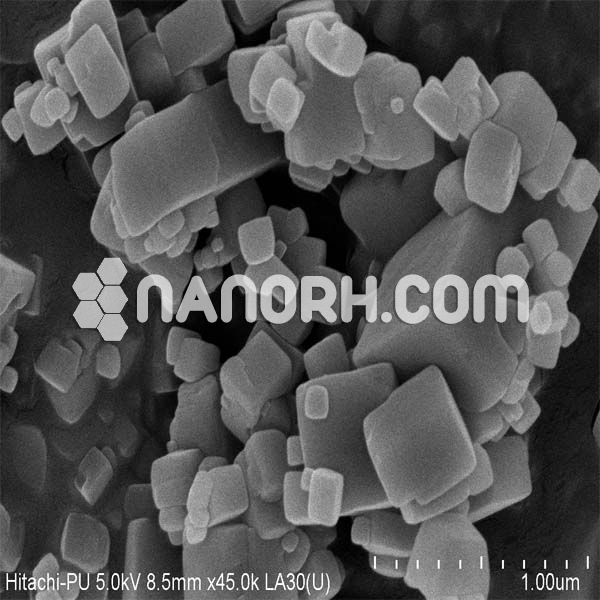
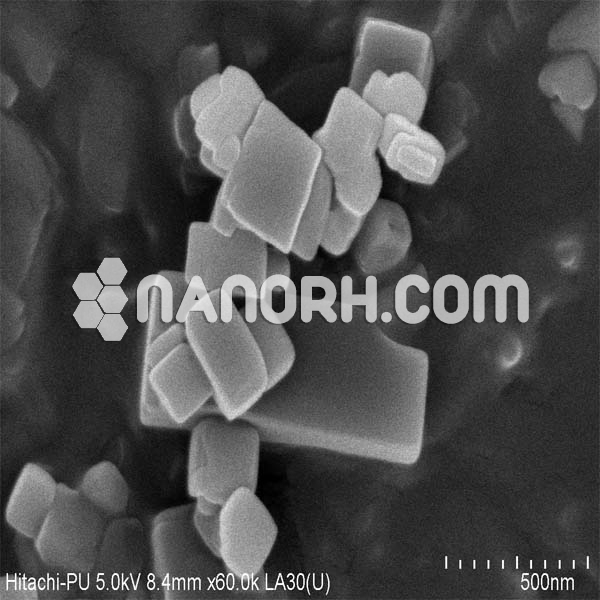
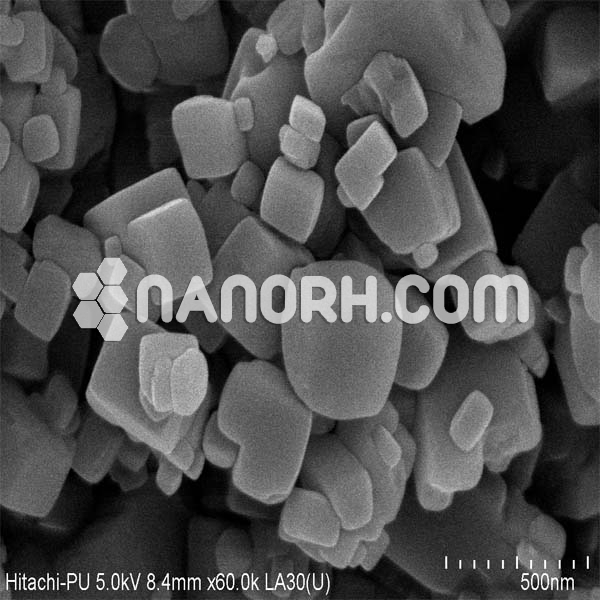
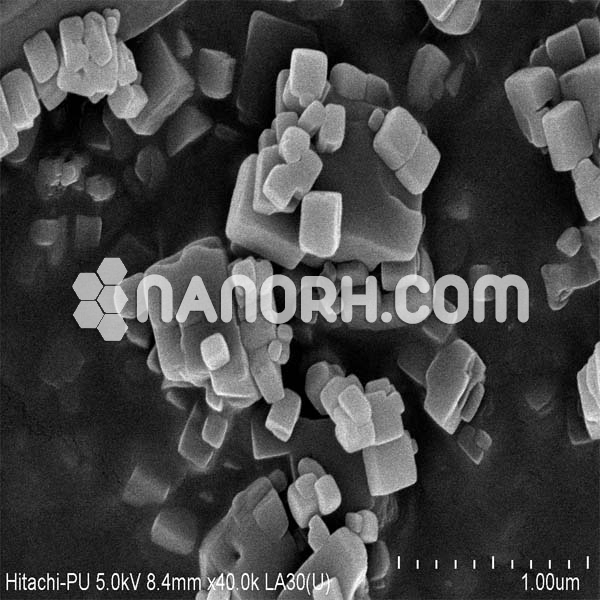
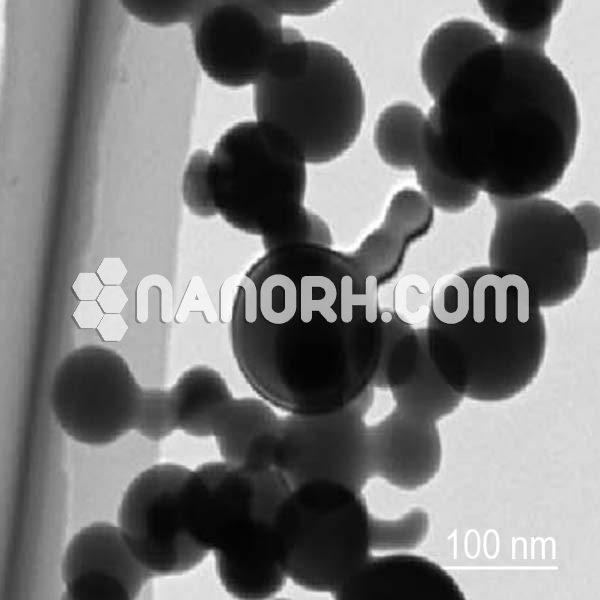
| Lithium Fluoride Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-5133 |
| CAS No. | 7789-24-4 |
| Formula | LiF |
| Density | 2.6 g/cm3 |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Melting Point | 845 °C |
| Molecular Weight | 25.94 g/mol |
Lithium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Introduction
Lithium Fluoride (LiF) Nanoparticles:
It forms a crystalline material with a high melting point, high ionic conductivity, and excellent thermal and chemical stability. In its nanoparticle form, lithium fluoride exhibits enhanced properties, including increased surface area, reactivity, and optical characteristics. These properties make LiF nanoparticles particularly useful in a variety of fields, including optical materials, energy storage, pharmaceuticals, and nuclear applications.
LiF nanoparticles are commonly synthesized using sol-gel methods, precipitation, or hydrothermal techniques, which allow for precise control over the particle size, morphology, and surface characteristics. The enhanced surface area and reactivity of LiF nanoparticles enable more efficient hydrogen bonding, adsorption of certain species, and improved luminescent properties compared to bulk LiF.
Properties of Lithium Fluoride (LiF) Nanoparticles:
High Thermal and Chemical Stability:
LiF has a high melting point (around 1,684°C) and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for applications that require resistance to high temperatures and harsh environments. Its chemical stability allows it to withstand exposure to both acidic and alkaline conditions.
Wide Bandgap and Optical Properties:
LiF has a wide bandgap (~12 eV), making it an ideal material for optical and electronic applications, especially those involving high-energy radiation. It is used in optical windows, phosphors, and luminescent devices.
Ionic Conductivity:
LiF is an ionic compound and exhibits high ionic conductivity, which makes it useful in solid-state batteries, electrolytes, and other energy storage systems. Its ionic conductivity can be enhanced in nanoparticle form, making it suitable for battery applications.