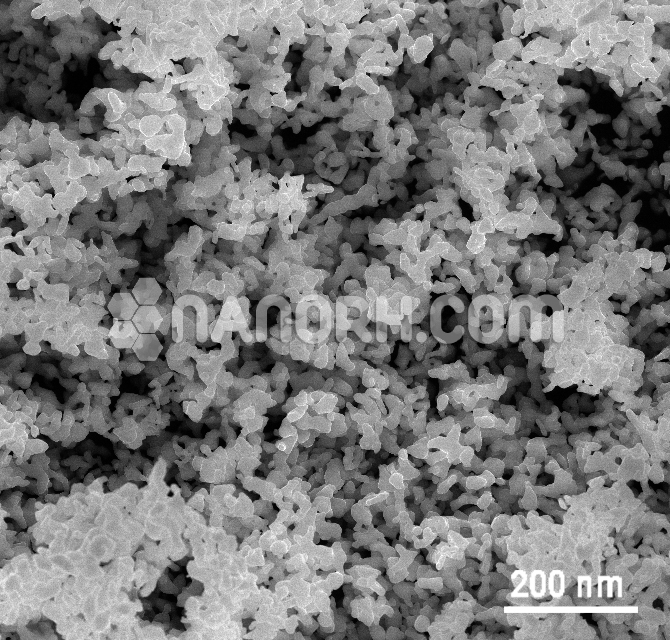
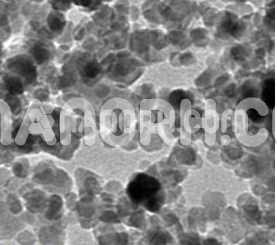
| Silver Nickel Alloy Nanoparticles |
|
| Product Number | NRE-2043 |
| CAS No. | 7440-22-4 / 7440-02-0 |
| Formula | Ag-Ni |
| Molecular Weight | 166.56 g/mol |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Colour | Gray |
| Density | Na |
| Melting Point | Na |
| Boiling Point | Na |
Nickel Silver Alloy Nanoparticles
Applications
Catalysis and Energy Systems
Catalytic Reactions: Nickel-silver alloy nanoparticles are gaining significant attention in heterogeneous catalysis for reactions such as hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, carbon-carbon bond formation, and oxidation reactions. These nanoparticles can facilitate industrial processes like fine chemical production, petrochemical refining, and biofuel production, where high catalytic efficiency is required. The synergistic effect of nickel and silver enhances the efficiency of these processes, especially in the production of clean fuels.
Fuel Cells and Energy Conversion: Nickel-silver alloy nanoparticles can serve as catalysts for fuel cells, particularly in reactions like the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR). The high conductivity and catalytic activity of these nanoparticles are crucial for improving the performance and efficiency of electrochemical energy systems, such as solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and hydrogen fuel cells. Their electrochemical stability under operating conditions makes them suitable for use in renewable energy technologies.
Batteries and Supercapacitors: The high conductivity and electrochemical stability of Ag-Ni make them promising candidates for energy storage devices, including batteries and supercapacitors. They are being studied for use in anodes, cathodes, and current collectors, where their high surface area and conductivity help improve the overall energy density, charge-discharge cycles, and efficiency of these devices.
Medical and Biomedical Applications
Antibacterial Coatings: The antimicrobial properties of silver are well-documented, and when incorporated into Ag-Ni, they offer enhanced protection against bacterial growth. These nanoparticles are being explored for use in wound dressings, medical devices, and catheters, where they can help prevent infections and reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). Their biocompatibility and non-toxicity make them an ideal choice for use in healthcare settings.